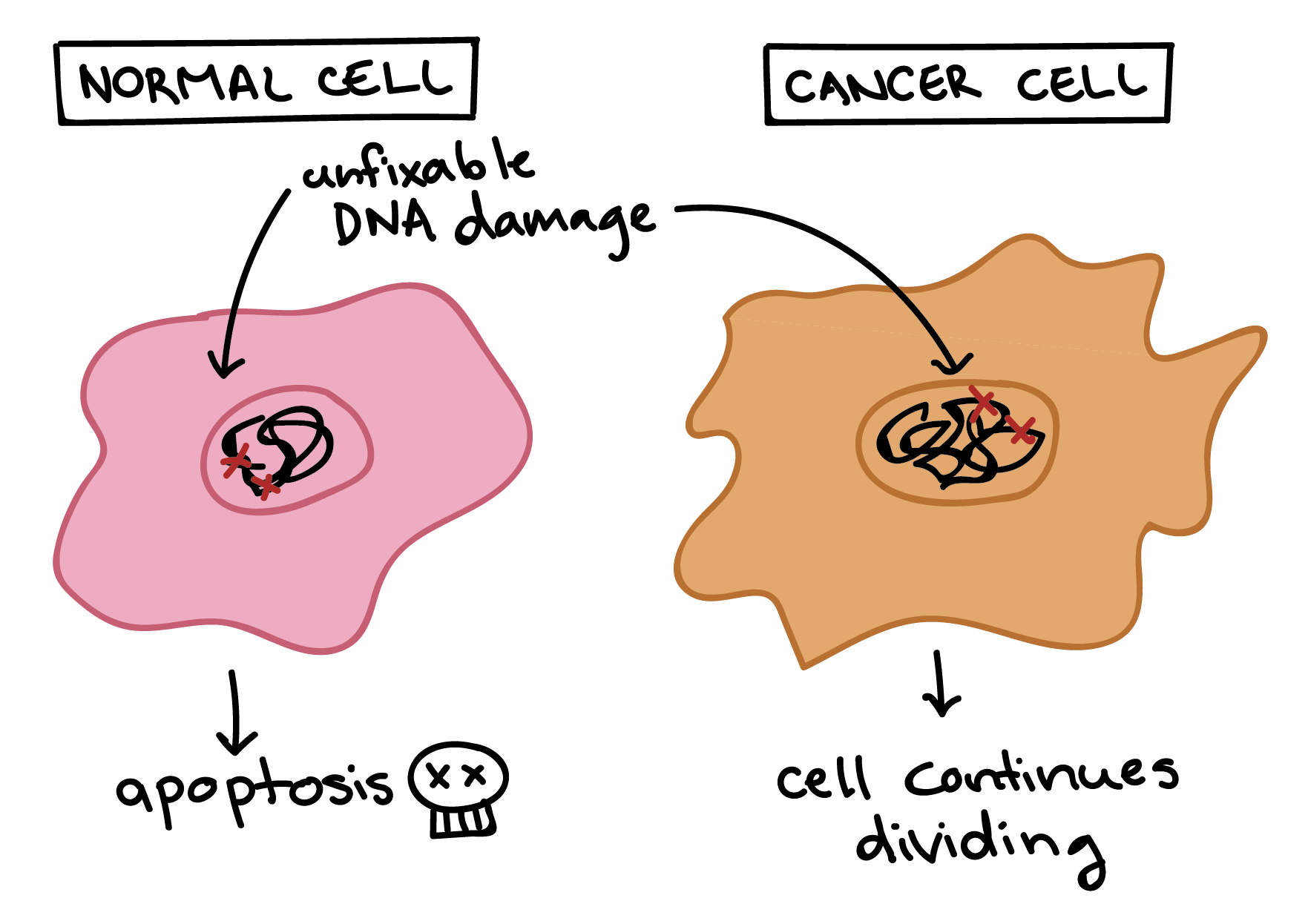
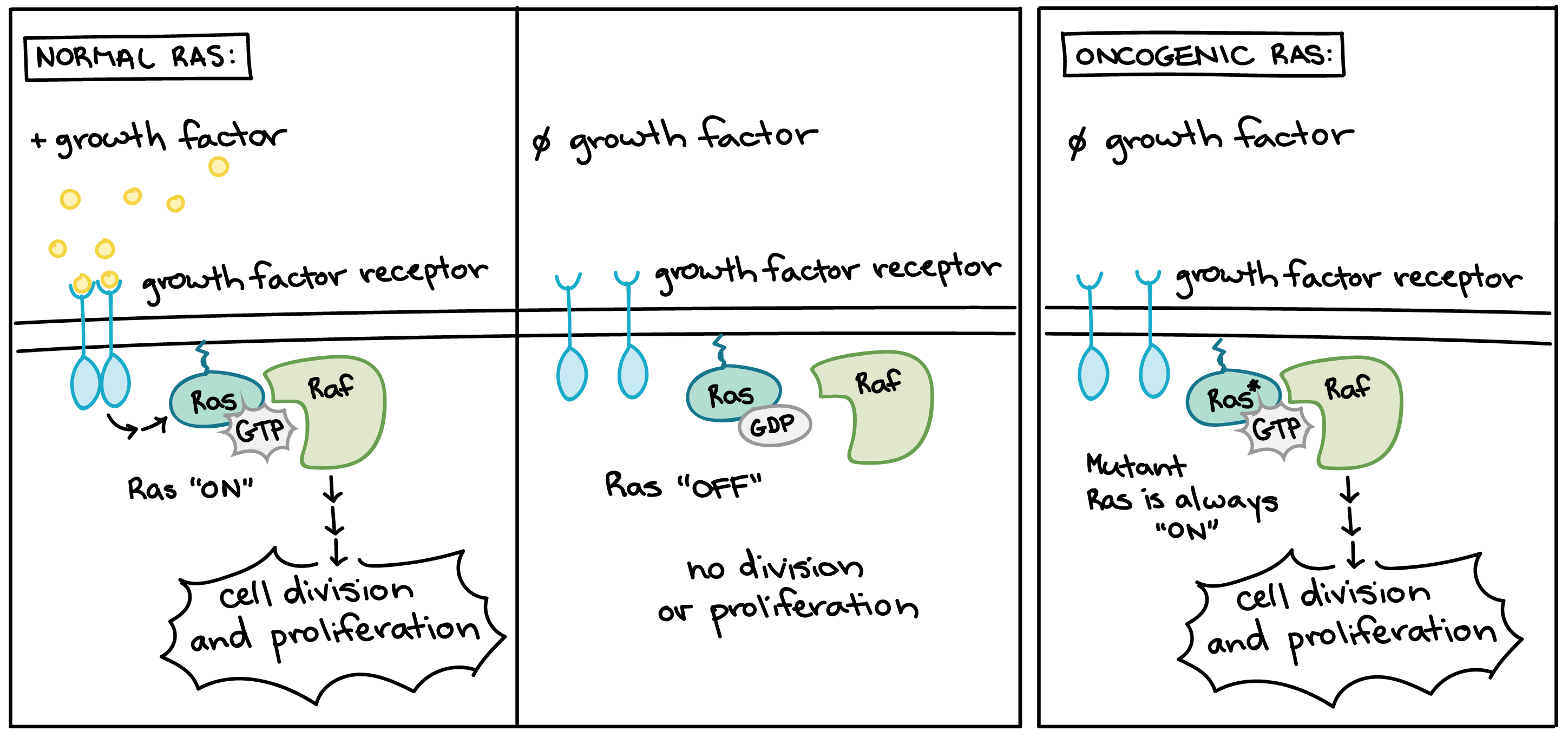
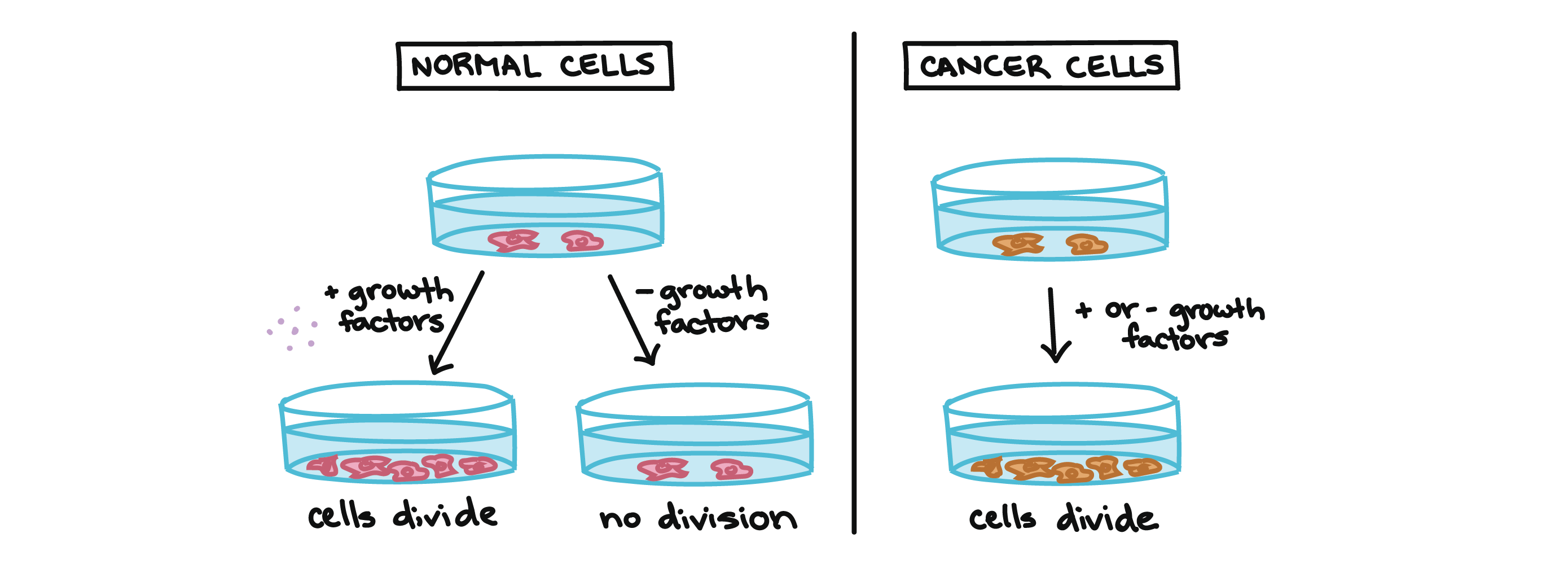
Describe the Rate of Division of Cancer Cells
Cancer cells can start to form when genes made up of DNA experience certain changes or mutations that cause the cells to behave abnormally. Begins when a single cell divides when it should not.

Mitosis Definition Stages Diagram Facts Mitosis Cell Division Somatic Cell
Rather than responding appropriately to the signals that control normal cell behavior cancer cells grow and divide in an uncontrolled manner invading normal tissues and organs and eventually spreading throughout the body.
. Normally human cells grow and multiply through a process called cell division to form new cells as the body needs them. Mitosis is a type of cell division which produces two identical diploid daughter cells. In 2000 cancer biologists Robert Weinberg and Douglas.
Originally tumours were thought to grow because they consisted of cells that multiplied more rapidly than cells in the surrounding tissue. In contrast to normal cells cancer cells often exhibit much more variability in cell sizesome are larger than normal and some are smaller than normal. Lets read more about cancer in vivo because it behaves completely different than immortalized cell lines in in vitro tests.
The fundamental abnormality resulting in the development of cancer is the continual unregulated proliferation of cancer cells. Cancer can start almost anywhere in the human body which is made up of trillions of cells. To replace aging and worn cells the body primarily uses a process called mitosis in.
The abnormality in cells can be progressive with a slow transition from normal cells to benign tumors to malignant tumors. These changes may be due to external factors such as tobacco smoke and ultraviolet rays. Most cells in the body go through a cycle of life in which their genetic information is retained fixed and passed down to daughter cells through a highly coordinated and regulated process.
Characteristics of Cancer Cells. Cancer is a disease in which some of the bodys cells grow uncontrollably and spread to other parts of the body. Traditionally chemotherapy destroys the diseased cells before they are replaced with healthy bone marrow from a donor.
The mutations may be inherited or completely random. B Identify the role of each experiment in determining the difference in how cancer and normal cells respond to EGF. G1 phase gap 1 phase is the first gap or growth phase in the cell cycle.
A mass of cells with no apparent function. Compare the mitotic rates for each cell type. Mutations in genes can cause cancer by accelerating cell division rates or inhibiting normal controls on the system such as cell cycle arrest or programmed cell.
In addition cancer cells often have an abnormal shape both of the cell and of the nucleus the brain of the cell The nucleus appears both larger and darker than normal cells. Its development and progression are usually linked to a series of changes in the activity of cell cycle regulators. Cancer is basically a disease of uncontrolled cell division.
Cancer cells grow and divide at an abnormally rapid rate are poorly differentiated and have abnormal membranes cytoskeletal proteins and morphology. The results published June 6 2018 in Nature suggest that by understanding how normal cells commit to cell division it may be possible to target this pathway in cancer cells and prevent them from dividing when they should not. In a fully grown adult of course the rate of cell proliferation is much less and under normal circumstances cell division in an adult takes place only when signals indicate the need to replace cells that.
The process used by a cell to copy itself is regulated so that a cell divides only when necessary and under the right conditions. Cancer cells depends on glycolysis for energy 6. For example inhibitors of the cell cycle keep cells from dividing when conditions arent right so too little activity of these inhibitors can promote cancer.
The S phase synthesis phase is period during which a cell. Select the true statements that describe cancer cells compared to normal cells. A fertilized egg divides into two cells which give rise to four and those give rise to eight and then to 16 and 32 and 64 and so on.
For cells that will divide again G 1 is followed by replication of the DNA during the S phase. Loss of Growth Control. C Calculate the mitotic index number of cells in mitosis divided by total cells for each kind of cell.
Cancerous tumours are either malignant or benign. The caps at the end of chromosomes that get smaller and smaller after each cell division except in cancer cells are called. Cell division and its role in cancer development.
Select all the reasons that cells need to control their rate of division. So we can assume that 124h is the maximum rate of cell division by cancer. See answer 1 Best Answer.
Ø When the normal cells grow in the tissue culture medium they grow and divide at a rate similar to that of cancer cells. Cancer is unchecked cell growth. Unregulated cell division leads to.
Cancer cells are protected from apoptosis 5. Normal cells have many controlling factors that allow them to divide on a regular basis or when needed but cancer cells have lost the ability to. What 2 treatments have been developed to destroy cancer cells.
Up to 24 cash back lead to uncontrolled cell division and growth of functionless cells. A Describe how EGF affects cell division. Cancer cells are monoclonal 1.
Describe the rate of division of cancer cells. Cancer cells have very high errors in DNA 4. Cancer cells undergo uncontrolled cell growth.
For example leukemia is a cancer that affects white blood cells. However during this cell cycle there are many situations where mistakes are made by the cycle or by a regulating system that causes the cell to proliferate uncontrollably leading to. What can cancer cells develop into.
A cell grows and carries out all normal metabolic functions and processes in a period called G 1 Figure 1.
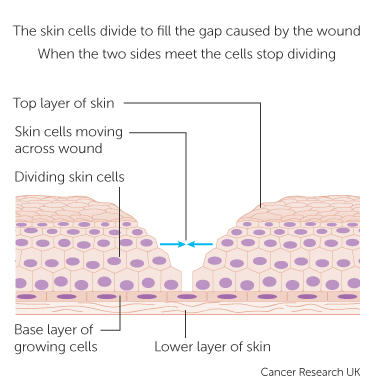
How Cells And Tissues Grow Cancer Research Uk
Cell Cycle Cell Division And Cytoplasmic Division

Cell Division Anatomy And Physiology
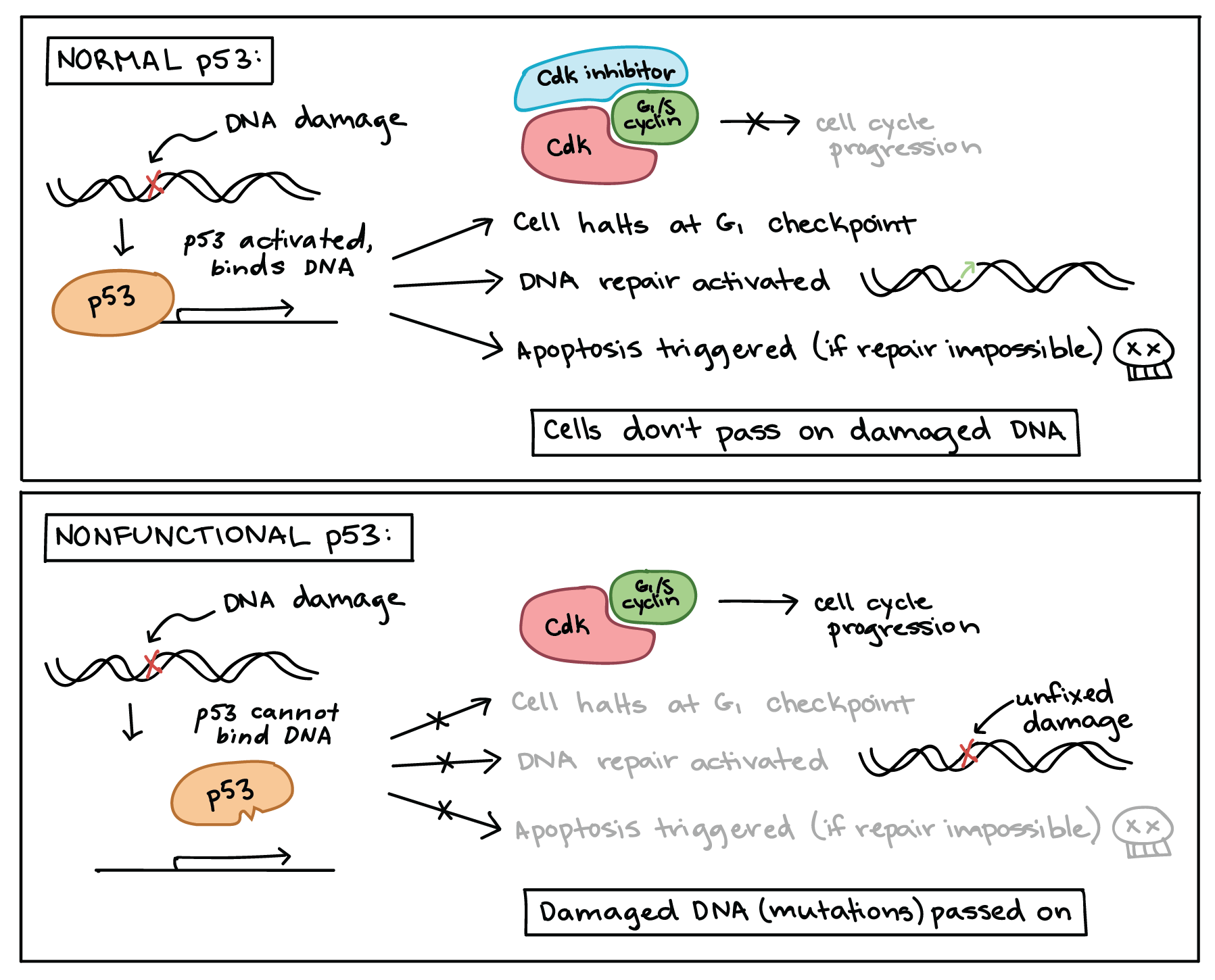
Cancer And The Cell Cycle Biology Article Khan Academy

Diabetes Lesson High School Biology Lessons Science Lessons High School What Is Diabetes Mellitus
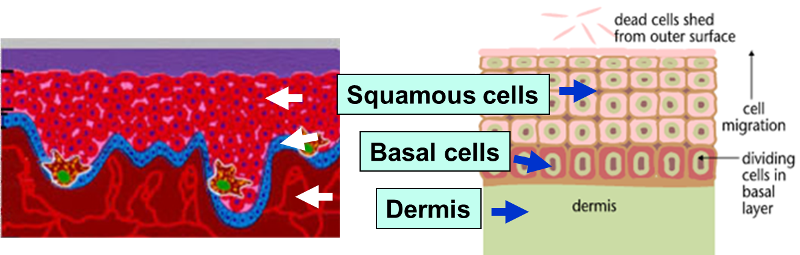
Normal Cell Division Growth Replacement

Normal Cell Division Growth Replacement
Normal Cell Division Growth Replacement

Cancer And The Cell Cycle Biology Article Khan Academy
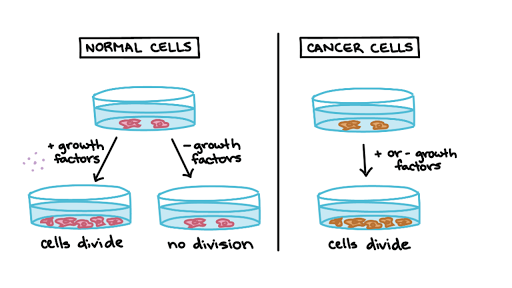
Cancer And The Cell Cycle Biology Article Khan Academy

How Cancer Starts Grows And Spreads Canadian Cancer Society

What Is A Telomere T A Sciences Telomeres Aging Science
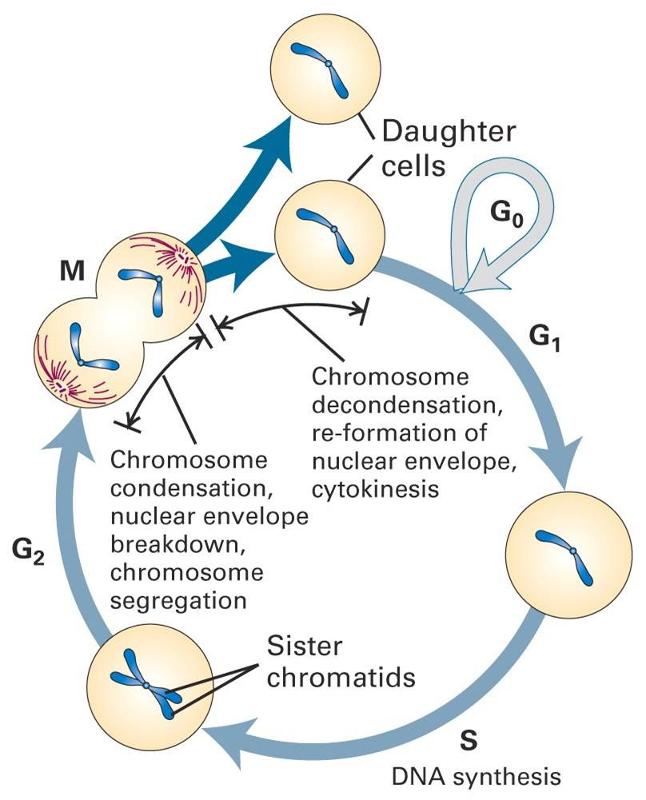
Normal Cell Division Growth Replacement